Companies that work in the Background to bring Semiconductors to Life

This the THIRD edition of our semiconductor newsletter series. In the FIRST edition, we journeyed through the fascinating history of semiconductors, from the invention of the first transistor to the rise of industry pioneers. The SECOND edition took us through the intricate value chain of semiconductor manufacturing, uncovering how a chip goes from concept to finished product. Today, we dive into the heart of the industry, examining the KEY COMPANIES that operate across EACH STEP of this value chain. We’ll explore their roles, the business models they’ve adopted, and the strategies they use to maximize value. Some of these companies may already be familiar to you, while others may be new discoveries. Together, these companies play a crucial role, both independently and collaboratively, in shaping the powerful devices we use every day. Before diving in, let’s look at an image that will help us recap what we learnt last week…
The Semiconductor Value Chain – FOUR Key Steps
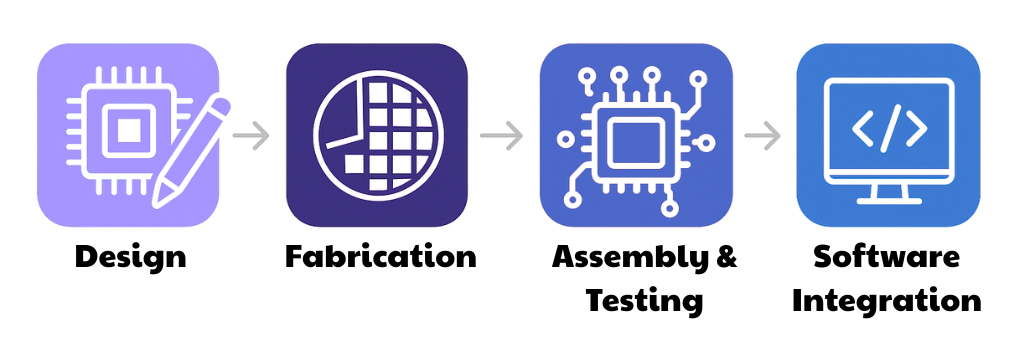
In the journey of exploring key players of the value chain, let’s start with the FIRST step, SEMICONDUCTOR DESIGN:
As we explored in our previous newsletter, chip design is one of the most complex and specialized aspects of creating the technology we rely on daily. When it comes to the players in this space, there are three key types to understand: 1) Chip Design Software Providers, who develop the tools that enable design; 2.1) Specialized Chip Architecture Designing & Licensing Companies, which focus on creating and licensing the blueprints for chips; and 2.2) Fabless Companies, which design chips but rely on third-party manufacturers to produce them.
1. Chip Design Software Providers: The Tools Behind Chip Design
Engineers and Designers use design software, also known as EDA (Electronic Design Automation) tools, to virtually test and create chips. These tools are essential in the chip design process, helping designers build complex chip blueprints and simulate their behavior in real-time.
These tools are the backbone of modern chip development. Without them, chip designers would be stuck trying to create these intricate designs manually, which would be both time-consuming and prone to mistakes.
Key Players – Synopsys (Market Cap ~$73 Bn), Cadence (Market Cap ~$81 Bn), Siemens EDA (formerly Mentor Graphics, Siemens’ total market cap ~$179 Bn). The combined market capitalization of these top EDA companies is ~$333 Bn.
Next, we move to the companies that use these tools to actually design chips. At this stage, companies can be divided in TWO types: 2.1) Specialized Chip Architecture Designing & Licensing Companies and 2.2) Fabless Companies.
2.1. Specialized Chip Architecture Designing & Licensing Companies
These companies design the core architecture, the blueprint of a chip and then license these designs to other companies. This makes it an industry standard for many devices we use today.
Why It’s Special: These companies don’t need to build factories or handle production costs. Instead, they earn in the form of royalties by licensing their designs to others, such as Apple and Qualcomm.
The Prime Example: A company called ARM is a prime example of such a company. In fact, ARM’s designs power everything from smartphones to laptops, servers,and automobiles, making it the industry standard. If you’re using a smartphone, laptop, or high tech car, chances are that ARM must have played a role in designed its chip.
Market Value: ARM’s market cap is ~$153 Bn, but its influence is enormous. ARM’s licensing model is highly profitable and powers billions of devices worldwide.
2.2. Fabless Companies
Meaning: Fabless companies are businesses that design semiconductors (chips) but don’t actually make them. Instead, they outsource the manufacturing process to specialized companies called foundries (which we’ll discuss next). These companies focus on the creativity and design.
They have mastered designing chips for various products, from smartphones to gaming consoles and AI systems. Their ability to focus on innovation while outsourcing production gives them the flexibility to lead in their respective fields and create new markets.
Key Players: NVIDIA (Market Cap ~$3.55 Tn), Qualcomm (Market Cap ~$169 Bn), AMD (Market Cap ~$206 Bn), Apple (Market Cap ~$3 Tn). The combined market cap of just these four fabless companies ~$7 Tn. Majority of the market cap belongs to Nvidia and Apple, the two largest corporations in the world.
The Interconnection of Chip Designers
There are inherent intricacies between these two types of designers because they are deeply connected. For example, ARM creates the fundamental blueprint (architecture) for chips, which it then licenses to fabless companies like Apple and Qualcomm. These fabless companies then tweak ARM’s design as per their specific needs, adding proprietary elements to create the final chip design. This finalized design is then sent to foundries for manufacturing.
Now, let’s move on to the next stage, SEMICONDUCTOR FABRICATION:
To put the importance of this step into context, fabrication is the heart of chip production. Each chip design that is made is eventually sent to foundries for production. Companies that are involved in this step can be divided in TWO categories, 1) Focused Foundry Operators and 2) Integrated Players. Apart from them, it is also important to know about players who supply hi-tech machines, specialized chemicals and other raw materials to manufacturers which enable them to produce power-packed chips that empower our devices today.
1. Focused Foundry Operators
Modus Operandi: Many giant companies that design chips, like NVIDIA, Qualcomm and Apple, outsource manufacturing to Focused Foundry Operators. These companies specialize in the manufacturing of semiconductors which are designed by fabless companies (like Qualcomm or Nvidia). Think of it like a bakery that doesn’t create the recipes (the designs) but bakes the cakes according to the recipes given by others. They operate large, advanced factories with cutting-edge technology to produce chips in large quantities for many different customers. They are experts in the manufacturing process, ensuring high quality and efficiency.
The reason why fables scompanies heavily depend on foundries for chip manufacturing is due to the following extreme realities:
Massive CAPEX: Building and maintaining a chip fabrication plant (“fab”) is extraordinarily costly, costs often run in billions of dollars. The specialized machines required are equally expensive and demand highly specialized skillset to operate Foundries invest tens of billions in cutting-edge technologies such as EUV lithography, enabling the production of smaller, more powerful chips (e.g.,7nm, 5nm, 3nm), making them the preferred choice for manufacturing hi-tech advanced chips.
Key Players: Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), controls 60%+ of global semiconductor manufacturing and Global Foundries.
Unmatched Scale: Foundries like TSMC produce chips at immense volumes, a scale individual fabless companies cannot afford to replicate. Their unmatched production capacity allows them to serve hundreds of customers and churn out billions of chips annually, meeting the massive global demand for semiconductors. This enormous production scale allows foundries to achieve significantly lower costs per unit, making their operations extremely efficient and cost-effective.
Deep Expertise: Chip manufacturing demands a highly specialized workforce with profound expertise in material science, nanotechnology, and electrical engineering. Foundries like TSMC have accumulated decades of experience, developing unparalleled know-how crucial for accurately and reliably manufacturing complex chip designs with billions of transistors. Their continuous innovation in areas like smaller fabrication nodes (e.g., 3nm, 5nm) and advanced packaging is incredibly challenging to replicate.
These technical, economical, and manufacturing capabilities allow Focused Foundries to produce the most high-tech chips at the scale customers require, and at the most effective cost possible. So, even if Apple or NVIDIA wanted to manufacture their own chips, they would most likely be unable to produce such high-tech chips at the required scale and cost.
2. Integrated Players
Despite the above mentioned complexities of the semiconductor industry, a few standout companies have successfully managed to integrate both SEMICONDUCTOR DESIGN and MANUFACTURING in-house and achieve immense success.
Key Players: Intel and Samsung Electronics
Intel designs its own chips (like Intel processors) and also operates its own foundries to manufacture these chips in-house. This makes Intel an Integrated Device Manufacturer (IDM), as it controls both the design and manufacturing processes. Samsung also follows a similar model. Samsung designs its own chips (like Exynos processors) and also operates foundries that produce chips, including those for other companies. Therefore, Samsung is also an IDM. In summary, Intel and Samsung are integrated players because they handle both chip design and manufacturing, unlike fabless companies that only design chips and outsource manufacturing to foundries.
Market Value: The combined market value of three foundries, TSMC, Samsung, and GlobalFoundries, is ~$1.2 Tn.
Before we move to the next step, let’s take a detour and talk about the machine and chemical providers to these foundries. This part of the value chain is also as concentrated as the foundry operation.
Machine Providers to Foundries
The machines used in semiconductor manufacturing, like photolithography, etching, and inspection machines, turn raw materials, such as silicon wafers, into functional chips. ASML (Netherlands) leads the EUV lithography market (with almost 100% market share), enabling the production of advanced chips at tiny sizes like 3nm. Additionally, Applied Materials and Lam Research provide essential tools for chemical deposition, etching, and cleaning, ensuring the chips are made with high precision. Their technologies are hard to replicate due to their complexity, high costs, and exclusive patents.
Chemical and Material Providers to Foundries
Foundries use specialized chemicals and materials to clean wafers, layer circuitry, and deposit gases. Companies like Merck, Air Products, and Dow Chemicals provide key materials, such as silicon wafers, gases, and cleaning chemicals, essential for making precise chips. The complexity of producing these materials, along with their strong global supply chains and years of research, makes it very hard for new companies to match their expertise.
Key Players – ASML (Market Cap ~$294 Bn), Applied Materials (Market Cap ~$136 Bn), Lam Research (Market Cap ~$116 Bn), Merck Group (Market Cap ~$55 Bn), Air Product (Market Cap ~$60 Bn), Dow Chemicals (Market Cap ~$20 Bn). The combined market value of machine and material provider to foundries is $681 Bn and are integral to the semiconductor industry.
Now, moving to step-three, ASSEMBLY, PACKAGING, & TESTING
A manufactured chip, initially, is just silicon which needs further steps to make it usable. It’s first assembled onto a base (substrate), then packaged in a protective cover, and rigorously tested for electrical performance and durability. These stages are vital for its correct function in any device.
While these steps may seem less glamorous than designing or manufacturing chips, they are critical for ensuring that chips work properly and can be safely used in devices like smartphones,computers, and cars.
Key Players: ASE Technology (Market Cap ~$20 Bn), Amkor Technology (Market Cap ~$5 Bn), JCET Group (Market Cap ~$8 Bn), Together, the combined market cap of these companies is around $33 Bn.
Now comes the last part of the value chain: SYSTEM INTEGRATION, bringing chips to life
After semiconductor chips are manufactured, they still require one final step (System/Software Integration) to become usable in real-world devices.
Once integrated, the chip connects to essential device components like the screen, battery, memory, etc. Softwares, including the operating system and drivers, are then optimized to work seamlessly with the chip for efficient task performance. Finally, the entire device is thoroughly tested to ensure all components and software function together are running smoothly.
These end function is carried out by none other than OEMs like Apple, Samsung, Microsoft, Dell, etc. These companies take the final chip products and integrate them into their devices, ensuring the chip works flawlessly with other components and the device’s operating software.
Conclusion
The semiconductor industry is a strange beast. Zoom into any one step, fabrication, chip design, packaging, and it feels like a monopoly. Just a handful of giants dominate, holding deep expertise, decades of IP, and near-insurmountable moats.
But zoom out, and it’s anything but lonely. The full chip-making process is a global relay race of hundreds of companies across dozens of countries passing the baton, each doing one ultra-specialised job to bring a chip to life.
It’s this bizarre mix of tight concentration and broad collaboration that makes semiconductors both incredibly powerful and incredibly fragile.
If you find this article feel free to share your thoughts on X, where you can find us as @bastionresearch.
Happy Investing!!!
🤣MEME OF THE WEEK🤣